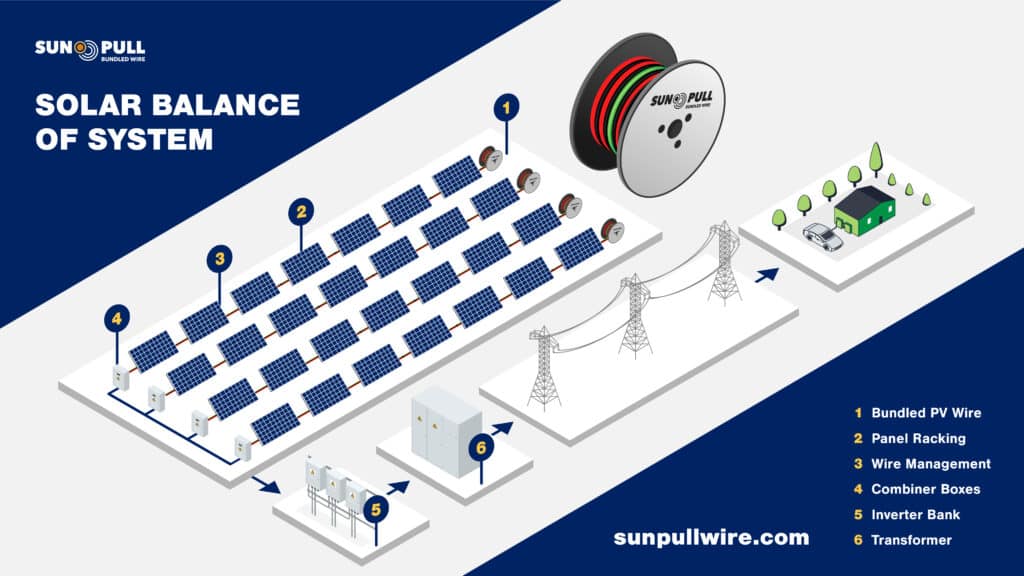
Balance of System for Utility Scale Solar

Utility scale solar systems consist of more than just photovoltaic panels. Planning for utility scale solar projects requires knowledge of all the components necessary to create an operational general project. These components are referred to as a balance of system, often abbreviated as BOS.
Most often, a balance of system refers to the components, equipment, structures, and services needed for the project beyond the PV modules themselves. A balance of system, besides the workmanship in the plant, determines the quality, safety, and profitability of the solar project since BOS components make up 50-60% of solar costs. Therefore, BOS components have a significant impact on the project’s overall costs and long-term profitability.
A solar PV balance of system is categorized into two groups: electrical and structural BOS. Here is a breakdown of these two categories and their applications in utility scale solar projects.
1. Electrical BOS
To deliver the energy generated from the sun to the grid, electrical BOS components are needed to allow the current to pass through the circuit. There are multiple electrical BOS components that are vital for minimizing electrical system losses.
- Inverters – inverters convert DC power produced by the solar array into usable AC power. These differ based on their costs, durability, and scale of the project. String inverters are more commonly used for utility-scale solar projects.
- Wiring – in a PV installation, DC cables are required for connection between the PV components while AC cables are used to connect the inverter to the grid. It is essential to pick the right type of wiring for PV installations that can withstand the outdoor conditions. Implementing cost-saving wiring solutions can also increase the profitability of a utility scale solar project.
- Combiner box – this combines multiple PV strings into a single circuit. Combiner boxes should be rated for outdoor applications and withstand extreme weather conditions.
- Fuses & Circuit breakers – these are primarily used to protect the system in fault conditions. They also are used to protect devices from catching fire or from becoming more seriously damaged if there is a short circuit.
- Grounding conductors – PV systems need to be grounded to protect people and equipment from electrical hazard and equipment damage. These include equipment grounding conductors (EGC), grounding electrode conductors (GEC), and rods. In special cases, PV systems need to be protected from lightning. That is also done through a special grounding electrode connected to the ground in order to drain the lightning current.
- Conduits – conduits provide damage protection for conductors. Conductors are better protected if they are run through conduits, raceways, and wireways not only for damage protection but also safety precautions. All conductors between a combiner box and the utility disconnects are usually run through conduits.
2. Structural BOS
Installation requirements vary from one solar project to another. However, they all need systems designed to hold them in place. These are referred to as structural BOS.
- Foundations – Solar panels require a strong, durable foundation. Foundation selection is critical for a cost-effective installation of PV solar panel support structures. There are four types of foundations commonly used such as driven piles, helical piles, earth screws, and ballasted foundations. The right foundation is based on the site conditions (such as the type of soil). Therefore, it is critical to thoroughly investigate the site of the project prior to picking the type of foundation.
- Racking – Racking systems are a crucial element of solar arrays. To fix solar panels to the ground, solar installation companies use solar racking products, also known as solar mounting, to hold solar equipment in place in the installation. Just like solar foundations, racking systems need to be optimal for the site conditions. With proper installation, a sturdy racking system secures the PV solar panels in extremely harsh weather conditions.
Utility-scale solar project needs vary from one solar project to another. Knowledge of the project needs, and the BOS components required are crucial for the project’s profitability. This also helps determine which BOS components are optional and which ones are necessary, ensuring a cost-effective and energy-efficient BOS environment.
Check out innovative solutions to cut down on the overall installation cost of utility scale solar.